Hip Replacement Surgery
What is Hip Replacement Surgery
While not everyone requires surgery, where surgery is recommended each patient’s treatment path is tailored to the patient’s individual needs.
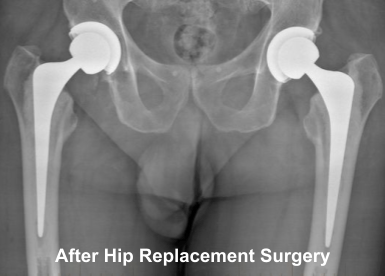
A total hip replacement (total hip arthroplasty) is a quality of life operation.
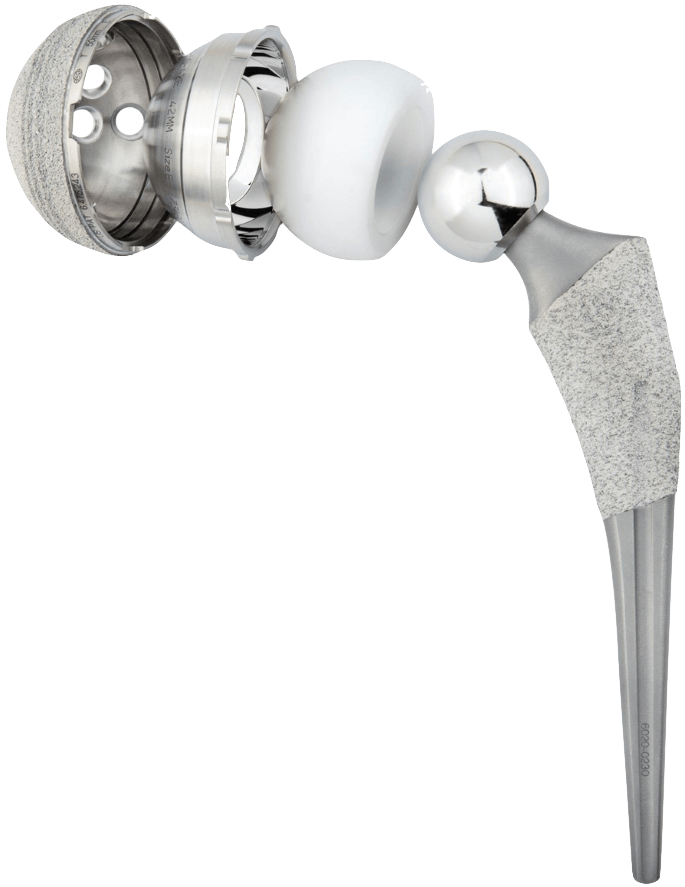
Hip Replacement Surgery involves the removal of the diseased joint and bone and a new ball and socket joint is inserted.
A hip replacement is one of the most successful operations that any orthopaedic surgeon does, and once done should last for decades (90% are still functioning after 20 years).
Hip replacement is indicated in patients with arthritis of the hip when the hip’s stiffness or pain limits a patient’s activities and quality of life
Who Is A Candidate For Surgery?
If you have severe arthritis of the hip causing pain and limitation of your activities and lifestyle and have not responded to conservative treatments you may be a candidate for total hip replacement.
Most hip replacement candidates are adults with degenerative disorders over the age of 50.
The procedure replaces part or all of the hip joint with an artificial device (prosthesis) which takes the place of the worn out ball and socket, the targeted results are:
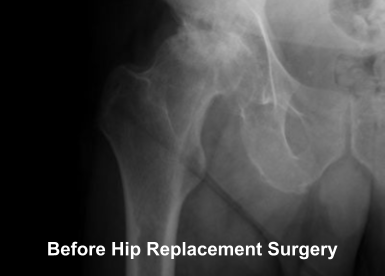
What is Arthritic Hip
Arthritis is a condition in which the articular cartilage that covers the joint surface is damaged or worn out causing pain and inflammation.
Some of the causes of arthritis include:
- Advancing age
- Congenital or developmental hip diseases
- Obesity
- Previous history of hip injury or fracture
- Increased stress on hip because of overuse
The degree of cartilage damage and inflammation varies with the type and stage of arthritis
- The cartilage lining is thinner than normal or completely absent.
- The capsule of the arthritic hip is swollen
- The joint space is narrowed and irregular in outline; this can be seen in an X-ray image
- Bone spurs or excessive bone can also build up around the edges of the join
A combination of these factors make the arthritic hip stiff and limit activities due to pain or fatigue.
Indications for Hip Replacement Surgery
For many patients hip arthritis symptoms may have been present for many months or even years. But after non-operative measures including weight loss, activity modification, regular analgesia are no longer effective, hip replacement can be considered.
Hip Surgery Recommendation
Once your surgeon and you have agreed on Hip Replacement Surgery your surgeon will often discuss the options available and what the patient’s preferences are. These may include the:
- Specific surgery type
- Hip implant
- Surgery Approach, and
- Surgery Method
These recommendations and the ideal approach to the hip depends on the individual patient’s anatomy, and your surgeon will advise you of the most appropriate hip replacement approach
Our aim is to return patients to their previous activity level with a fully functioning pain-free hip joint. This includes a return to high impact and velocity sports, e.g. running, skiing, tennis.
Types of Hip Replacement Surgery
The types of Hip Replacement Surgical choices can include:
- Total Hip Replacement
- Partial Hip Replacement
- Hip Resurfacing
- Revision Surgery
Hip Replacement Approaches
There are three main surgical approaches for Hip Surgery. The different surgical approaches vary in several ways but essentially come down to the way a surgeon cuts the soft tissues to get to the hip. At Align both anterior and posterior hip replacement is performed, depending on the patients' need and surgeons preference.
A well-done hip replacement is a fantastic operation, in terms of pain relief and improved quality of life, regardless of which approach is used, the significant difference between the two approaches is the position of the scar!
Hip Replacement Implants
There are many different types of artificial joints prosthesis available, all made from different materials and offering different bearing surfaces.
- Traditional Implants
- Dual Mobility Implants - suitable for both Posterior and Anterior approaches
Surgical Methods
Minimally Invasive Surgery
The most common Hip Replacement surgical method is minimally invasive. This technique involves inserting the implant through a minimally invasive muscle splitting, tissue-preserving surgical incision.
The approaches goal is to reduce any tissue damage and improve recovery time and outcomes.
Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery
Accurate alignment of the hip components is critical to the overall function and improved outcomes after Hip surgery.
Your surgeon employs Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) that utilises robotic or image-guided technologies that help to accurately pinpoint anatomical landmarks that can be difficult with small incisions.
Further the system can help navigate through different bone cuts and implantation alignment.
How Your New Hip Is Different
Your new hip may activate metal detectors required for security in airports and some buildings. Tell the security agent about your hip replacement if the alarm is activated.
After surgery, make sure you also do the following:
- Participate in regular light exercise programs to maintain proper strength and mobility of your new hip.
- Take special precautions to avoid falls and injuries. Individuals who have undergone total hip replacement surgery and suffer a fracture may require more surgery.
- Notify your dentist that you had a hip replacement. You should be given antibiotics before all dental surgery for at least 3 months postoperatively.
Your Treatment Journey
Please see us periodically for a routine follow up examination and X-rays.
It is important that you contact our office directly after discharge if you have any concerns whatsoever about your operation and progress.
We will always be available to answer any queries.